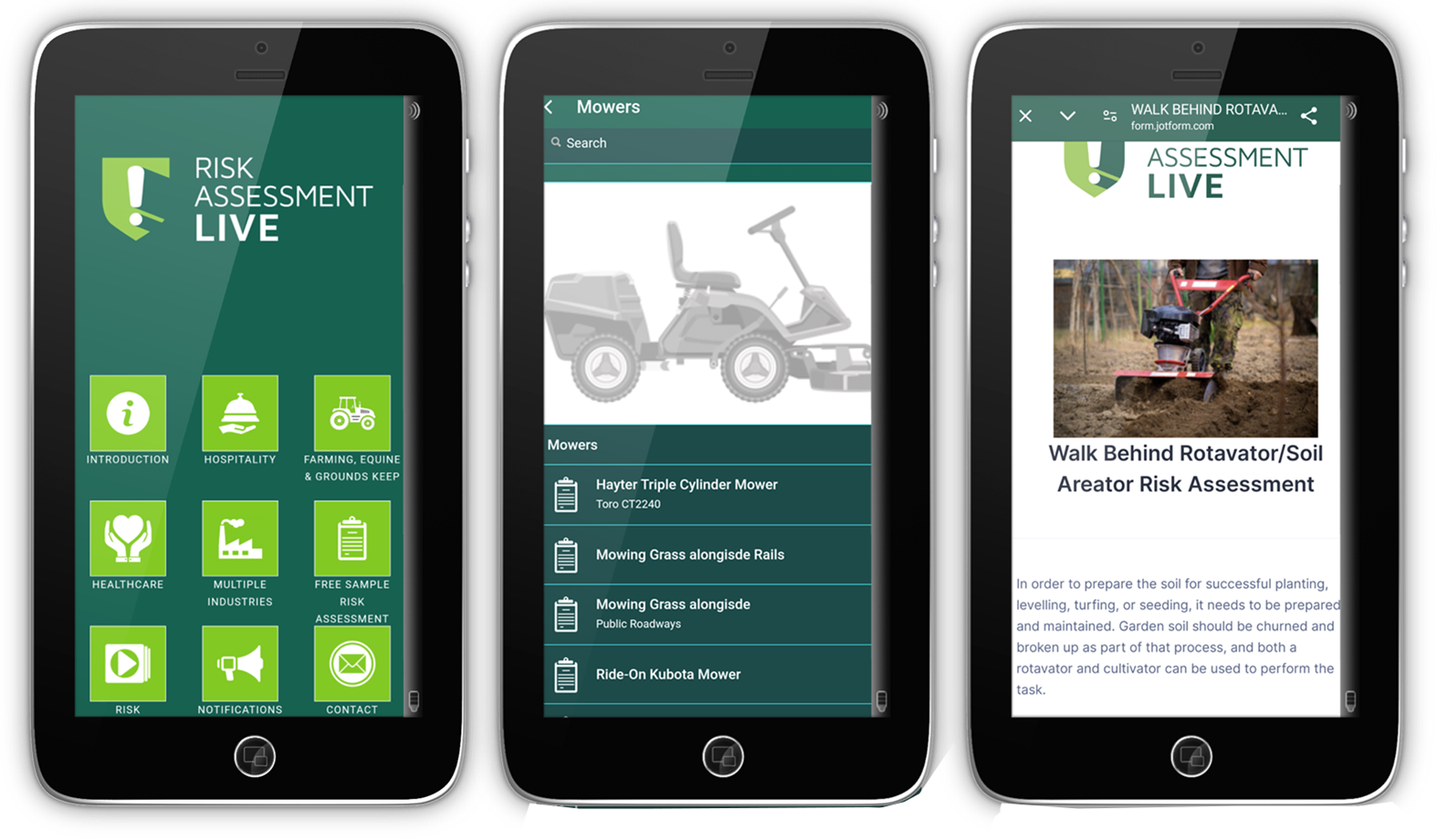
Understanding the Main UK Health and Safety Regulations
What Business Owners Need to Know
Health and safety regulations in the UK are designed to protect employees, customers, and the general public from risks associated with workplace activities. As a business owner, you have a legal duty to comply with these regulations to prevent accidents, reduce liability, and create a safe working environment.
Failure to comply with health and safety laws can lead to severe penalties, including fines, prosecution, and reputational damage. This guide provides an overview of the key UK health and safety regulations you need to be aware of and how to ensure compliance.
1. Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 (HSWA)
The Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 is the cornerstone of workplace safety law in the UK. It places general duties on employers, employees, and the self-employed to ensure the health, safety, and welfare of all individuals affected by workplace activities.
Key Duties for Employers:
- Conduct a suitable and sufficient risk assessment of workplace hazards.
- Provide safe systems of work, equipment, and training for employees.
- Ensure adequate welfare provisions, such as first aid and sanitation facilities.
- Maintain clear and accessible health and safety policies.
- Appoint a competent person to oversee health and safety compliance.
Failure to comply can lead to enforcement action by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), including fines and criminal prosecution.
2. The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 (MHSWR)
These regulations expand on the HSWA and provide more detailed requirements for managing workplace risks.
What Business Owners Must Do:
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Identify potential hazards, evaluate risks, and implement control measures.
- Appoint Competent Persons: Assign individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills to manage health and safety.
- Provide Training & Information: Employees must receive adequate health and safety training relevant to their job roles.
- Establish Emergency Procedures: Have clear plans for fire safety, evacuations, and first aid.
Businesses with five or more employees must document their risk assessments and health & safety policies.
3. Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations 1992
These regulations focus on maintaining a safe and healthy work environment.
Key Requirements:
- Adequate Ventilation & Temperature Control: Workplaces must be well-ventilated and maintain a reasonable temperature.
- Safe Work Surfaces: Floors, stairs, and passageways must be well-maintained to prevent slips and trips.
- Welfare Facilities: Provide toilets, washing facilities, drinking water, and rest areas.
Non-compliance can result in legal action, particularly if poor workplace conditions lead to injuries.
4. The Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER)
These regulations ensure that any work equipment used in businesses is safe to operate and well-maintained.
What You Need to Do:
- Ensure equipment is fit for purpose and used only by trained employees.
- Conduct regular inspections and maintenance.
- Provide protective measures such as guards, emergency stop mechanisms, and warning signs.
Industries using machinery, tools, and vehicles must be particularly diligent in PUWER compliance.
5. The Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations 1992 (PPE Regulations)
These regulations require employers to provide suitable Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) where necessary.
Business Owner Responsibilities:
- Identify job roles requiring PPE (e.g., construction, healthcare, manufacturing).
- Ensure PPE is free of charge, well-maintained, and properly stored.
- Train employees on how to use and care for PPE.
Recent updates emphasize that PPE must also be provided to self-employed workers and contractors.
6. The Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002 (COSHH)
COSHH governs the safe handling of hazardous substances such as chemicals, dust, and biological agents.
Compliance Steps:
- Identify hazardous substances used in your business.
- Implement control measures, such as ventilation, PPE, and safe storage.
- Train employees on handling hazardous substances safely.
- Conduct regular health surveillance where necessary.
Businesses in sectors like cleaning, manufacturing, and healthcare must strictly follow COSHH guidelines.
7. The Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations 2013 (RIDDOR)
RIDDOR requires businesses to report certain workplace incidents to the HSE.
Reportable Incidents Include:
- Work-related fatalities.
- Serious injuries like fractures or loss of limbs.
- Occupational diseases such as asbestosis.
- Dangerous occurrences, such as explosions or equipment failures.
Failure to report incidents can result in fines and legal repercussions.
8. Fire Safety Legislation (Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005)
This law requires businesses to assess and manage fire risks.
What Business Owners Must Do:
- Conduct a fire risk assessment and implement control measures.
- Provide fire-fighting equipment, alarms, and escape routes.
- Assign a responsible person to oversee fire safety.
- Train staff on fire evacuation procedures.
Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including imprisonment in extreme cases.
9. Working at Height Regulations 2005
These regulations protect workers from falls and injuries when working at height.
Key Employer Duties:
- Avoid working at height where possible.
- Use suitable equipment (e.g., scaffolding, harnesses, guardrails).
- Ensure proper inspection and maintenance of height-related equipment.
- Train workers in safe working at height practices.
These rules are especially crucial in construction, roofing, and maintenance industries.
10. Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992
This regulation covers lifting, carrying, pushing, and pulling activities.
How to Ensure Compliance:
- Conduct risk assessments for manual handling tasks.
- Provide lifting aids like trolleys or mechanical hoists.
- Train staff in safe lifting techniques.
Ignoring manual handling risks can lead to musculoskeletal injuries and liability claims.
Ensuring Compliance: Practical Steps for Business Owners
- Stay Informed: Keep up to date with changes in legislation by following HSE guidance.
- Appoint a Health & Safety Officer: Assign someone to oversee workplace safety.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Identify and mitigate hazards proactively.
- Train Employees Regularly: Ensure all workers understand their responsibilities.
- Document Everything: Keep records of risk assessments, training, and safety measures.
- Engage with External Audits: A third-party review can help identify compliance gaps.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and complying with UK health and safety regulations is essential for every business owner. A proactive approach not only ensures legal compliance but also enhances workplace morale, reduces accidents, and protects your business from fines and reputational damage.
Investing in robust health and safety policies and training will ultimately create a safer, more productive working environment for everyone.
Need Help With Health & Safety Compliance?
If you need expert guidance, risk assessment templates, or professional training for your team, get in touch with a qualified health and safety consultant today.

Health & Safety Made Simple
CONTACT
Tel No: 01223 258156
Email: trevor@cambridgesafetysolutions.com
All Rights Reserved | Risk Assessment.Live